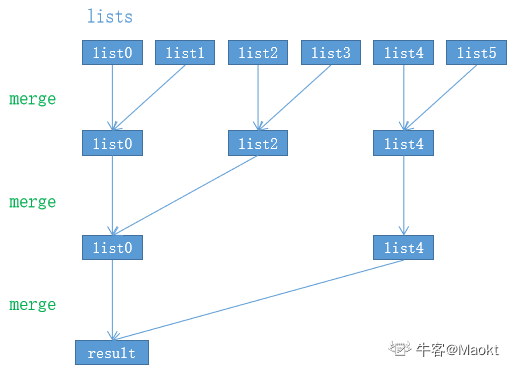
描述
数据范围:节点总数满足 0≤n≤10^5 ,链表个数满足1≤k≤10^5 ,每个链表的长度满足1≤len≤200 ,每个节点的值满足 |val| <= 1000
要求:时间复杂度 O(nlogk)
输入:
辅助数组 解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution : def mergeKLists (self , lists ): tmp = [] for head in lists: while head: tmp.append(head.val) head = head.next if not tmp: return None tmp.sort() res = ListNode(-1 ) cur = res for i in range (len (tmp)): cur.next = ListNode(tmp[i]) cur = cur.next return res.next
顺序合并 解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import java.util.*;public class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists (ArrayListlists) { return mergeList( lists , 0 , lists.size() - 1 ); } public ListNode mergeList (ArrayListlists , int L ,int R) { if (L == R){ return lists.get(L); } if (L > R){ return null ; } int mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1 ); return merge( mergeList(lists,L,mid) , mergeList(lists,mid+1 ,R)); } public ListNode merge (ListNode l1 , ListNode l2) { if (l1 == null || l2 == null ){ return l1 = = null ? l2 : l1; } ListNode dummy = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode cur = dummy; while ( l1 != null && l2 != null ){ if (l1.val < l2.val){ cur.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; }else { cur.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } cur = cur.next; } cur.next = (l1 == null ? l2 : l1); return dummy.next; } }
优先队列 解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import heapqclass Solution : def mergeKLists (self , lists ): dummy = ListNode(0 ) p = dummy head = [] for i in range (len (lists)): if lists[i] : heapq.heappush(head, (lists[i].val, i)) lists[i] = lists[i].next while head: val, idx = heapq.heappop(head) p.next = ListNode(val) p = p.next if lists[idx]: heapq.heappush(head, (lists[idx].val, idx)) lists[idx] = lists[idx].next return dummy.next
self 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.List;import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists (ArrayList<ListNode> lists) { List<Integer> tmp = lists.stream().map(v -> { List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList <>(); while (v != null ) { temp.add(v.val); v = v.next; } return temp; }) .flatMap(List::stream) .collect(Collectors.toList()); Collections.sort(tmp); ListNode result = new ListNode (-1 ); ListNode p = result; for (Integer integer : tmp) { p.next = new ListNode (integer); p = p.next; } return result.next; } }